World Heart Day 2022: 70% Of Heart Attack Deaths In India Last Year Occurred In 30-60 Age Group
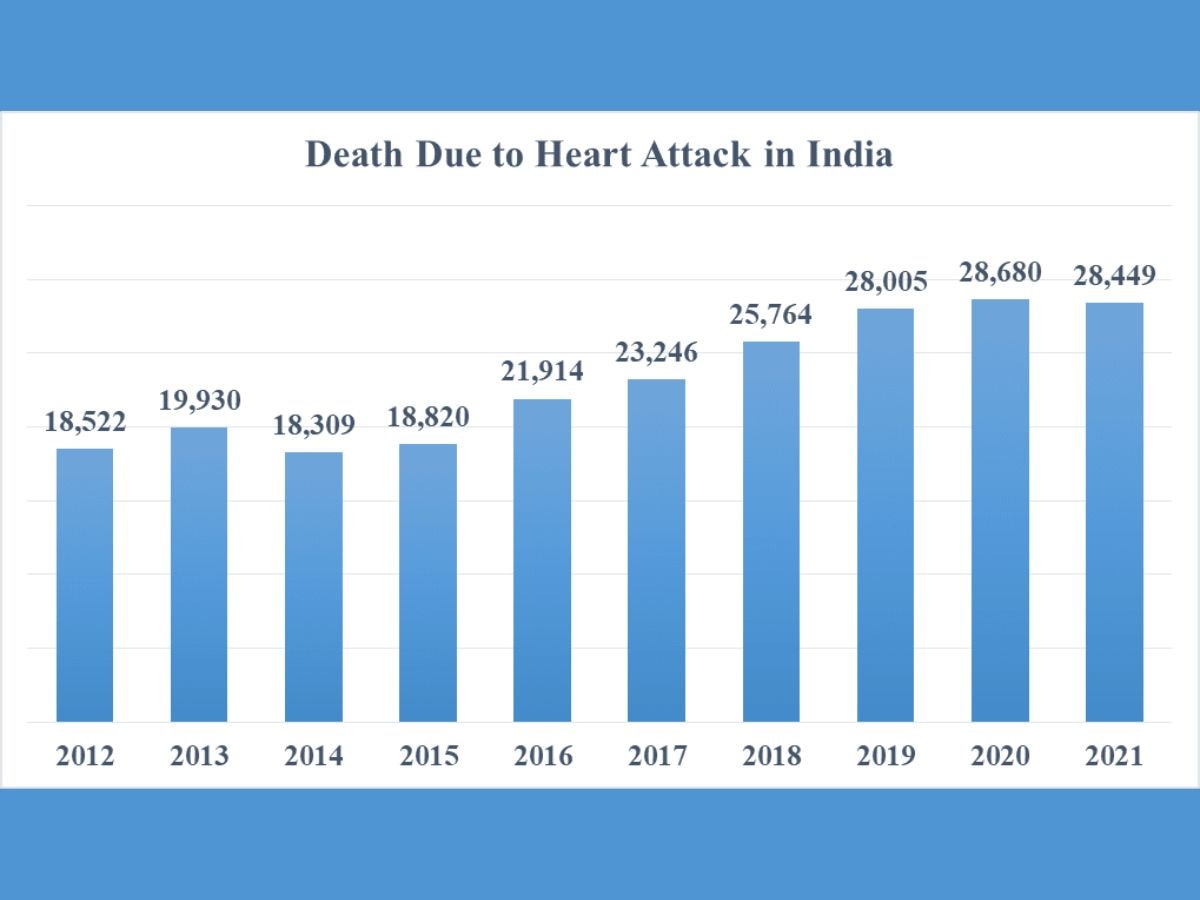
World Heart Day 2022: The number of deaths due to heart attacks in India has remained consistently over 25,000 in the last four years, and over 28,000 in the last three year.

World Heart Day is observed every year on September 29. The number of deaths due to heart attacks in India has remained consistently over 25,000 in the last four years, and over 28,000 in the last three years, according to data on "Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India" (ADSI) compiled by the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB).
The number, however, fell marginally from 28,680 in 2020 to 28,449 in 2021. India had begun Covid-19 vaccination on January 16, 2021.
Heart attack deaths over the years
There was no significant increase in deaths due to heart attack in 2021 over 2019. The number of heart attacks in 2021 were 1.6 per cent more than that during 2019. Also, the number of deaths due to heart attacks in 2021 was less than that in 2020. From 2017 to 2021, there was a 22 per cent increase in death due to heart attacks. In the last 10 years, from 2012 to 2021, there had been a 54 per cent increase in heart attack deaths, according to the NCRB.
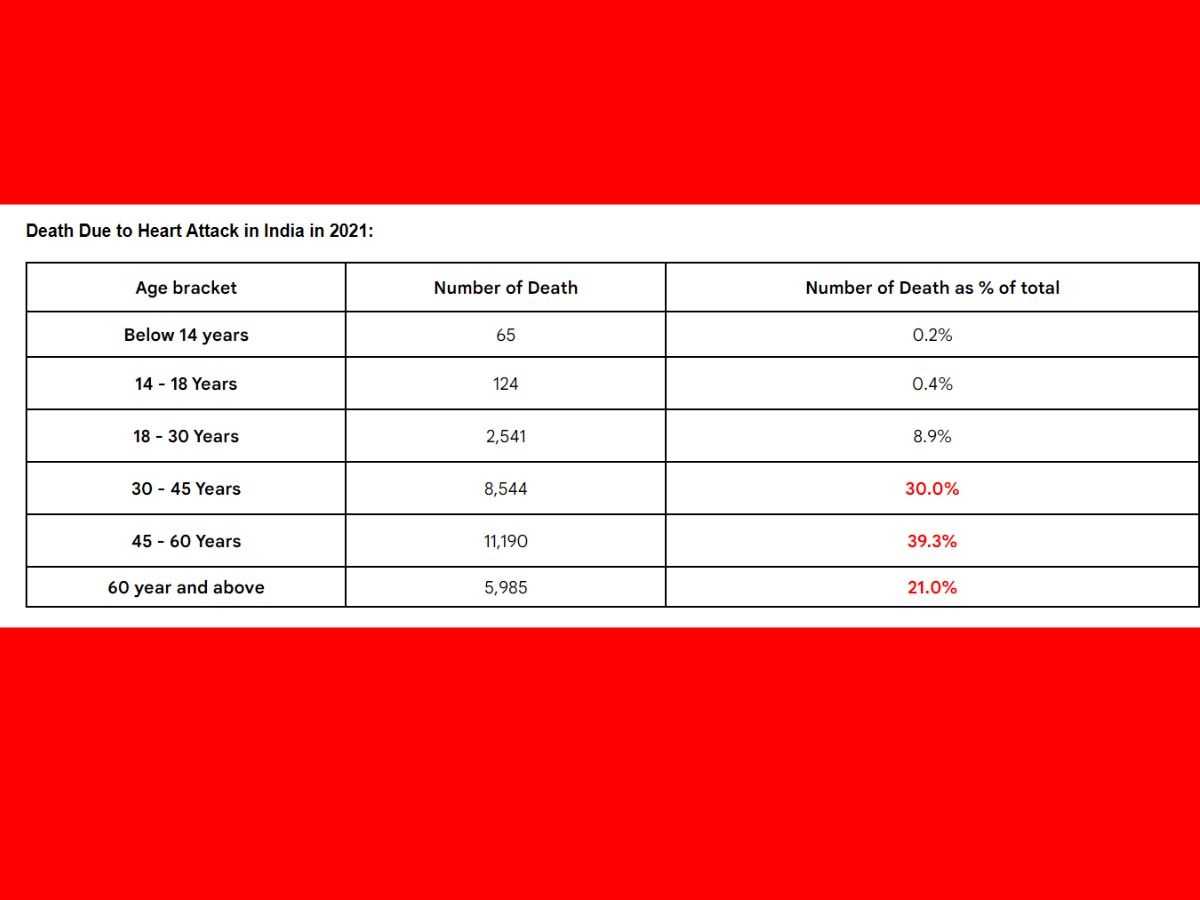
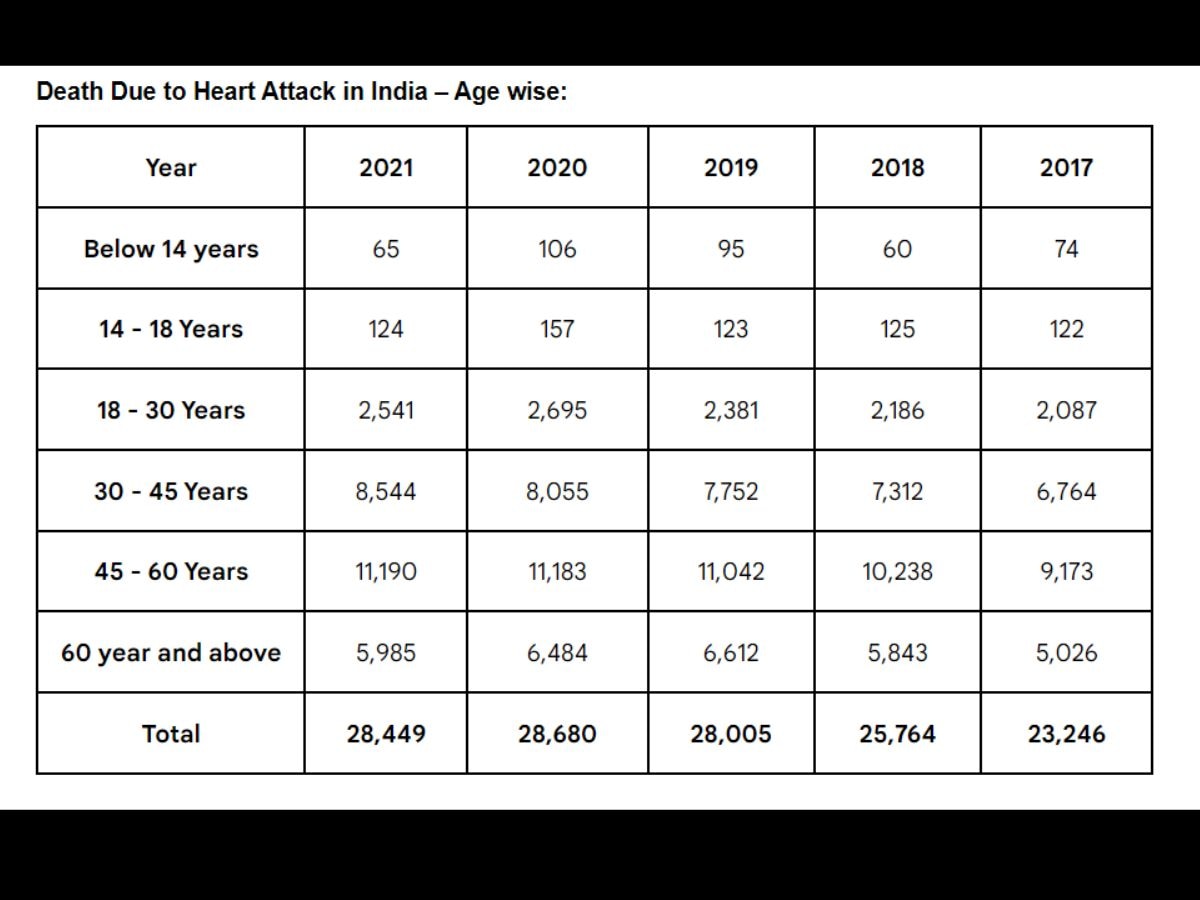
Last year, 70 per cent of heart attack deaths occurred in the 30-60 age group. A total of 19,744 people aged 30 to 60 years died due to heart attacks in 2021.
People belonging to the age group of 45 to 60 years were most prone to heart attack deaths, followed by those aged 30 to 45 years. The reasons include lifestyle, increased physical labour, and high stress.
In 2020, the total number of deaths from heart attack in people aged 30 to 60 years in India was 19,238. There was an increase of over six per cent in the number of heart attack deaths in this age group, from 2020 to 2021.
The number of people aged 18 to 30 years who died from heart attacks in India was 2,541 in 2021, and 2,695 in 2020. This means that heart attack deaths in this age group decreased by 0.057 per cent from 2020 to 2021.
Link between Covid-19 and Heart Attacks
COVID-19 can affect any system in the body, primarily the lungs and then, the heart, Dr Bikram Kesharee Mohanty, Senior Consultant Cardio-Throacic & Vascular Surgeon (Adult & Paediatric) and Visiting Consultant at National Heart Institute, New Delhi, told ABP Live.
He said that as long as the involvement of the heart is concerned, it could be because of reasons include lack of oxygen, stress cardiomyopathy, and immune reaction triggered by Covid-19 infection, among others. Stress Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscles caused by the release of stress enzymes inside the body.
Since the lungs are involved, they cause the heart to work more vigorously to meet the oxygen demand of the body, Dr Mohanty explained.
“The viral infection can affect the heart as a whole (heart muscles) by causing inflammation and, thereby, damage to the organ, which is known as myocarditis.
Cytokine storm and immune reaction triggered by the COVID virus infection wherein cytokine is released by the immune system in response to the infection, thereby damaging the body tissue and heart muscles,” he said.
Why death from heart attacks in India decreased between 2020-2021 after the rollout of Covid-19 vaccines
Dr Mohanty explained that death from heart attacks decreased from 2020 to 2021 because people came to know that Covid-19 was an additional risk factor for the heart, and patients with heart ailments were at greater risk, as a result of which an awareness was created about the importance of heart health.
“There is no direct relation between the COVID vaccine and fewer heart attacks; however, after COVID vaccination, the consequences of heart involvement decreased because of the role of the vaccine in lessening the severity of infection as a whole in every system of the body,” he said.
Heart Attack: Causes
The heart needs to be supplied with oxygen-rich blood to function properly, similar to other organs in the body. Coronary arteries supply blood to the heart. Unhealthy dietary habits and lifestyle lead to the development of fatty deposits or plaque on the walls of the coronary arteries.
As plaque builds up in the heart over time, it can lead to blockage, preventing blood in the arteries from reaching some parts of the heart muscle.
This results in cardiac ischemia, a condition where a portion of the heart is deprived of oxygen. If this is not treated in time, the heart tissues begin to die, leading to a heart attack, or myocardial infarction.
ALSO READ | World Heart Day 2022: Excessive Exercise Is Not Good For Our Bodies, Brings A Heavy Load On Heart
Heart Attack: Signs
The signs of heart attack include chest pain that may feel like tightness or squeezing, pain that spreads to the shoulder, arm, back, neck, jaw, teeth, and sometimes, the upper belly, cold sweat, fatigue, heartburn, indigestion, light-headedness, sudden dizziness, nausea, and shortness of breath, among others.
A sudden cardiac arrest is sometimes the first sign of a heart attack.
ALSO READ | EXPLAINED: Signs Of Cardiac Arrest And Immediate Steps That Should Be Taken
Heart Attack: Immediate steps to be taken
If one has a sudden heart attack, those nearby should give the person a tablet of aspirin, ideally 300 milligrams, unless he or she is allergic to aspirin. This is because aspirin helps thin the blood vessels, and improves blood flow to the heart.
Heart Attack: How to prevent myocardial infarction
One can prevent heart attacks by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, consuming a healthy and balanced diet, quitting smoking, losing weight, exercising regularly, reducing alcohol consumption, managing stress, monitoring blood pressure and blood sugar levels, and incorporating low-fat, high-fibre foods in the diet.
If one has high blood cholesterol levels, they should take medicines such as statins. Also, people should consume foods such as wholegrains, fruits and vegetables every day.
ALSO READ | Why You Should Consume Three Grams Of Omega-3 Fatty Acids Everyday
The people at risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular disease must regularly consult the doctor, and undergo screening as advised. The different screening techniques include electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, angiogram, cardiac computed tomography (CT) scan, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
ALSO READ | Risk Of Death Higher For Those Who Cannot Stand On One Leg For 10 Seconds, Study Finds
What is a cardiac arrest?
"Cardiac arrest" and "heart attack" are terms often used interchangeably, but are not the same. Since both can result in death, it is important to know the signs of a cardiac arrest and heart attack, and seek immediate medical help.
A cardiac arrest is the abrupt loss of heart function in a person who may or may not have been diagnosed with heart disease, and can come suddenly or in the wake of other symptoms. If appropriate steps are not taken immediately, a cardiac arrest can be fatal.
ALSO READ | EXPLAINED: The Difference Between A Cardiac Arrest And A Heart Attack
Cardiac Arrest: Signs
A person is said to have a cardiac arrest when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood around the body, according to the British Heart Foundation. When the heart stops pumping blood, the brain is deprived of oxygen, causing the person to fall unconscious and stop breathing.
Certain types of arrhythmias, which prevent the heart from pumping blood, result in cardiac arrests. A heart arrhythmia is an irregular heartbeat.
(With Amod Prakash Singh)
Check out below Health Tools-
Calculate Your Body Mass Index ( BMI )
Calculate The Age Through Age Calculator






































