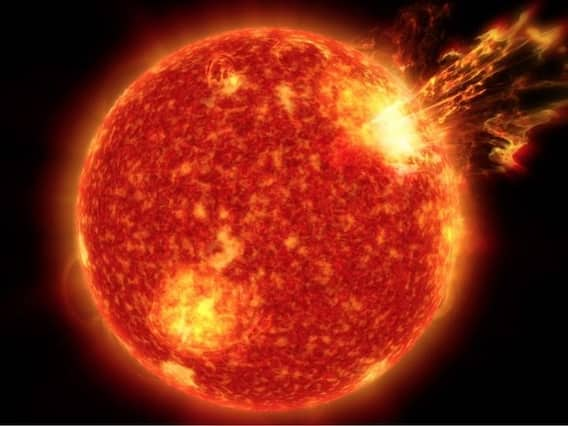
New Delhi: The "corpse" of an old sunspot exploded on Monday, April 11, 2022, unleashing plasma towards Earth.
The unexpected eruption of the "dead sunspot", called AR2987, released loads of energy in the form of radiation, which resulted in a coronal mass ejection (CME), according to spaceweather.com. Sunspots are dark areas on the solar surface which contain strong magnetic fields that are constantly shifting.
The CME is expected to reach Earth on Thursday, April 14. The impact of the CME could trigger a G2-class or moderate geomagnetic storm, according to SpaceWeather.
Also, a G1-class or minor geomagnetic storm is likely to impact Earth on Friday, April 15, 2022, according to the Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC) of the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
A G1 (minor) geomagnetic storm watch has been issued for April 15, 2022, as CME effects persist into the 15th, the SWPC said on its website.
A storm watch means that severe weather has not occurred yet, but upcoming weather conditions are expected to result in potentially dangerous weather.
What Is A Geomagnetic Storm?
A geomagnetic storm is a major disturbance in the Earth's magnetosphere (area of space around a planet, that is controlled by the planet's magnetic field) which occurs when there is a very efficient exchange of energy from the solar wind into the space environment surrounding Earth. Variations in the solar wind produce major changes in the currents, plasmas, and fields in Earth's magnetosphere, which, in turn, result in geomagnetic storms.
ALSO READ | Largest Icy Comet Nucleus Ever Seen Is Bigger Than US State Of Rhode Island, Confirms Hubble
Based on measurements made by ground-based instruments which observe how much the horizontal component of Earth's magnetic field varies, the geomagnetic storms are categorised from G1 (minor) to G5 (extreme).
What Is A Coronal Mass Ejection?
Coronal mass ejections or CMEs are large expulsions of plasma and magnetic fields from the Sun's corona, or the outer solar atmosphere.
These large clouds of solar plasma and embedded magnetic fields are released into space after a solar eruption.
How Could A G2-Class Or Moderate Geomagnetic Storm Impact Earth?
A G2-class or moderate geomagnetic storm can impact Earth's power systems, and hinder spacecraft operations.
For instance, high altitude power systems may experience voltage alarms, according to SpaceWeather. Transformers may be damaged due to long-duration solar storms.
Since the solar storm can impact spacecraft operations, ground control may have to perform corrective actions to properly orient different spacecraft.
The geomagnetic storm can also cause high frequency radio propagation to fade at higher latitudes.
The disturbance in Earth's magnetosphere can result in breathtaking auroras in regions located at lower latitudes, such as New York and Idaho.
ALSO READ | How Climate Change Is Leading To Birds Laying Eggs Earlier Than Normal